All Posts
-
- May 22, 2025 1
What is the role of the thermometer in healthcare simulation?
In healthcare simulation, the thermometer plays a crucial role in enhancing realism and enabling learners to practice clinical decision making based on vital signs. Its key roles include:
- Simulating Vital Signs: A thermometer allows learners to measure and interpret body temperature, which is an essential component of a patient’s vital signs.
- Supporting Scenario Fidelity: Including realistic temperature data helps create more believable clinical scenarios, improving the authenticity and educational value of the simulation.
- Teaching Clinical Skills: Learners practice proper technique for temperature measurement (oral, tympanic, rectal, axillary, or temporal), which is critical in real-life patient assessments.
- Triggering Clinical Decisions: Abnormal temperatures (e.g., fever, hypothermia) can prompt learners to consider and manage potential underlying conditions such as infection or sepsis.
- Evaluating Learner Response:
-
- May 20, 2025 8
Which medications are most represented in medical simulation?
In medical simulation training, the focus is on preparing healthcare professionals for common, high-stakes, or emergency situations. The most represented medications tend to fall into the following categories:
1. Emergency and Critical Care Medications
These medications are heavily featured in simulations involving cardiac arrest, trauma, sepsis, or anaphylaxis.
- Epinephrine – used in cardiac arrest, anaphylaxis, and severe asthma.
- Atropine – used in bradycardia and some poisoning scenarios.
- Amiodarone – for arrhythmias.
- Lidocaine – another antiarrhythmic, also used in local anesthesia.
- Naloxone (Narcan) – for opioid overdose.
- Adenosine – for supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).
2. Anesthetics and Sedatives
Used in surgical and airway management simulations.
- Propofol – sedative used in intubation and procedural sedation.
- Midazolam – benzodiazepine used for sedation and seizures.
- Fentanyl – for pain control, often in conjunction
-
- May 19, 2025 11
What is INACSL 2025?
The International Nursing Association for Clinical Simulation and Learning (INACSL) will host its annual conference, INACSL25, from June 19 to 22, 2025, at the Sheraton Denver Downtown Hotel in Denver, Colorado.
INACSL25 serves as a premier forum for simulation specialists, researchers, educators, and solution providers to exchange state-of-the-art knowledge in simulation operations, skills, and applications within an evidence-based framework. inacsl.org
Conference Schedule Highlights
- Thursday, June 19: Morning and afternoon workshops and SIMS tours (additional registration required), followed by the grand opening of the Exhibit Hall with poster viewing.
- Friday, June 20: Keynote presentation, concurrent sessions, SIG Rush, Professor Rounds poster tours, and an Exhibit Hall reception.
- Saturday, June 21: Hayden Vanguard Keynote & Awards Ceremony, concurrent sessions, and the INACSL Celebration Reception.
- Sunday, June 22: Final concurrent sessions and an endnote presentation.
-
- May 18, 2025 8
What types of stethoscopes are commonly used in healthcare simulation?
In healthcare simulation, several types of stethoscopes are commonly used, depending on the level of realism and interactivity required. Here are the main types:
- Standard Acoustic Stethoscopes
- These are the same as those used in clinical settings.
- Used mainly for basic auscultation practice on manikins or standardized participants (SPs).
- Examples: Pocket Nurse® single-head or dual-head stethoscopes, Sprague stethoscopes, and more
- Electronic or Digital Stethoscopes
- Amplify sound and often allow for recording and playback.
- Useful in simulations requiring auscultation of subtle or abnormal sounds.
- Examples: Cardionics E-Scope II and Hearing-Impaired E-Scope
- Simulated (Bluetooth/Wi-Fi Enabled) Stethoscopes
- Paired with high-fidelity manikins or simulation software.
- Learners hear programmed heart, lung, or bowel sounds via the device.
- Example: Cardionics SimScope®
- Augmented Reality (AR) or Smart Stethoscopes
- Integrated with
- Standard Acoustic Stethoscopes
-
- May 18, 2025 5
Which programs are needed when starting a Phlebotomy education program?
Starting a phlebotomy education program requires a mix of clinical, instructional, and administrative supplies to ensure students can learn both theory and hands-on techniques safely and effectively. Here's a categorized list of essential products you'll likely need:
Clinical Supplies (Hands-on Practice)
These are the tools students use to practice blood collection and related techniques.
- Vacutainer blood collection sets (needles, holders, tubes)
- Butterfly needle sets (for small or difficult veins)
- Tourniquets (disposable and/or reusable; latex-free available)
- Alcohol prep pads and antiseptic wipes
- Gauze pads and bandages
- Sharps containers (OSHA-compliant)
- Gloves (non-sterile, various sizes)
- Lancets (for capillary blood sampling)
- IV training arms/manikins (for practice draws)
- Simulated blood
- Biohazard disposal bins and bags
Lab & Simulation MaterialsUsed for mock lab settings and blood analysis simulations.
- Vacuum
-
- May 18, 2025 1
What are the most popular types of gloves for medical simulation?
In medical simulation, gloves are used to replicate real-world clinical settings and ensure realism during training. The most popular types of gloves for medical simulation are:
- Nitrile Gloves
- Most common choice due to their durability, flexibility, and resistance to punctures and chemicals.
- Latex-free, making them suitable for people with latex allergies.
- Latex Gloves
- Offer excellent tactile sensitivity, which is important for procedures that require fine motor skills.
- Still used in some simulations despite allergy concerns, particularly for realistic training.
- Vinyl Gloves
- Cost-effective and used in low-risk training scenarios.
- Not as durable or form-fitting as nitrile or latex but good for general-purpose simulation tasks.
- Simulated Surgical Gloves
- Designed to mimic sterile surgical gloves used in the OR.
- Used in advanced simulations such as surgeries or sterile procedures.
- Nitrile Gloves
-
- May 18, 2025
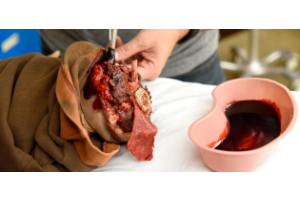
What types of products are used to teach ostomy care?
Teaching ostomy care involves a mix of real and simulated products to help learners become comfortable with handling ostomies. Here are the common types of products used in training:
1. Ostomy Training Manikins & Models
- Manikins with stoma models: These are life-size or partial-body models with one or more stomas (colostomy, ileostomy, urostomy) to simulate real-life care.
- Wearable simulators: Some are designed to be worn by standardized participants (actors) to mimic real ostomy situations.
2. Ostomy Appliances
- Pouching systems:
- One-piece and two-piece systems (both drainable and closed end)
- Skin barriers and flange systems
- Adhesive rings or wafers
3. Stoma Care Supplies
- Cleansing wipes and skin prep products
- Barrier pastes, powders, and sprays
- Deodorizing products
- Measuring guides (to size the stoma and cut pouches appropriately)
- Scissors and application tools
4. Educational Kits and Sample Packs
- Often provided by manufacturers
-
- May 18, 2025 5
What is the importance of sterile gloves in medical simulation?
Sterile gloves are important in medical simulation for several key reasons:
- Realism and Skill Development: Using sterile gloves in simulations helps learners practice correct aseptic techniques, which are essential for preventing infections in real clinical settings. This realism enhances muscle memory and helps form habits of best practice.
- Preparation for Clinical Practice: It allows students and professionals to become comfortable with the feel and handling of sterile gloves, which can be tricky to don and use properly without contamination.
- Reinforcement of Infection Control Principles: Even though no real patients are involved, maintaining sterile technique in simulation reinforces the importance of infection control protocols.
- Confidence Building: Practicing with sterile gloves in a low-stress, simulated environment boosts confidence before transitioning to high-stakes clinical settings.
- Assessment of Competency
-
- May 18, 2025 13
What gauges of needles are used for different medical procedures?
Needle gauges vary depending on the medical procedure and the type of fluid being injected or withdrawn. The gauge refers to the diameter of the needle — the higher the gauge, the thinner the needle. Here's a general guide to common needle gauges and their uses:
-
- May 18, 2025
What is the role of manikins in healthcare simulation?
Manikins play a crucial role in healthcare simulation by providing a realistic, hands-on way for students and professionals to practice medical procedures, clinical decision making, and teamwork in a safe, controlled environment. Here's a breakdown of their key roles:
- Skill Development: Manikins allow learners to practice procedures like CPR, intubation, catheter insertion, wound care, and more – without risk to real patients.
- Scenario-Based Training: High-fidelity manikins can simulate complex medical conditions (e.g., heart attacks, trauma, childbirth) to train teams in diagnosing and responding to emergencies.
- Error Management: The use of manikins in simulation activities gives healthcare workers the opportunity to make, recognize, and learn from mistakes in a no-risk setting.
- Teamwork & Communication: Manikin-based simulation activities support interprofessional training, helping teams develop coordination, leadership, and



Validate your login
Log In
Create New Account